WoSign OTP Authentication System
The initiative for Open Authentication (OATH) is the top OTP solution architecture standard constitutor in the world, who collaborates with top authentication system providers aimed at providing universal strong authentication across all users and all devices over all networks.
Proudly being the professional information security provider listed as the contributing partner of OATH, WoSign Technologies has introduced the WoSign OTP Authentication System (WOAS) solution to enterprises. By integrating OTP authentication solutions with the application system, business can gain the advantage of introducing two-factor authentication for users, thus maintain a higher level of security than using simple and unsafe static passwords.
The WoSign OTP server Authentication System (WOAS), as a mature OTP solution, works with plenty well-known authentication systems under the most popular platforms, which is well equipped with a full range of WoSign OTP tokens.
All being OATH compliant, WoSign OTP tokens cover the whole group of One-Time Password generation mechanisms from event-synchronous, time-synchronous, and challenge-response to the EMV CAP-based reader featuring One-Time-Password authentication for users and online transaction.
Introduction
The WoSign OTP Authentication System (WOAS) provides comprehensive authentication services to businesses, meanwhile streamlines all authentication operations such as deployment, provisioning and maintenance in order to reduce the IT overhead to the utmost.
The WOAS architecture, as shown in the figure on the right, includes the following main components:
- The authentication service/SDK
- The authentication agent/SDK
- The OTP management tool (management center)
As well as the three supplementary parts:
- The database system
- The application system
- The OTP tokens
With the help of the WOAS, business can gain higher competitiveness with improved trust from end-users and build up a better image in providing advanced security.
Benefits
The WOAS brings advanced benefits for customers such as:
- Multiple database and server OS support
- Customizable OATH complaint OTP tokens
- Full range of OTP tokens from event synchronous, time synchronous to challenge-response and EMV-CAP smart card reader
- Industry-specific authentication solutions at reasonable price
- Package-ready or flexible authentication solutions
- Seamless integration solution with existing third-party authentication systems
The following are a few of specifications of the WOAS.
Specification
| No. | Technical Parameter | Description |
| No. | Technical Parameter | Description |
| 1 | Amount of users supported | More than 10 million |
| 2 | Throughput per authentication server | <5ms |
| 3 | Bandwidth used for authentication | <1MB |
| 4 | Disaster prevention for authentication data | Backup via cluster |
| 5 | Disaster prevention for authentication data | Backup via cluster |
| 6 | Out-of-band authentication | 2-channel authentication |
| 7 | Supported protocols | RADIUS, LDAP, TCP/UDP, and SOAP |
| 8 | Supported operating systems | IBM AIX, HP-UX, Windows, Linux, and Unix |
| 9 | Supported database systems | Oracle, DB2, Sybase, SQL Server, My SQL, PostgreSQL, MSDE, and Access |
| 10 | Supported length of dynamic password | 6 digits/8 digits |
| 11 | Authentication Server API interface | C/C++, Java, Web Service and more |
| 12 | Authentication agent API interface | C/C++, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, PHP and more |
WOAS Scheme
- VPN/Terminal Server Authentication
- Outlook Web Access Protection
- Domain Access Protection
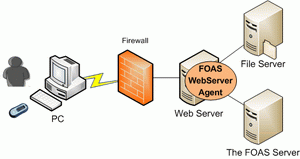
- Web Server (Apache/IIS) Protection
- Single Sign On
VPN/Terminal Server Authentication
Network devices (most VPN, firewalls, routers or exchange servers) support standard RADIUS protocol. Other application servers can use this solution as far as they support standard RADIUS protocol. When an end-user wants to login, the OTP generated by the OTP token will be sent to the WOAS server through the VPN server based on standard RADIUS protocol. The WOAS server will then return the authentication result to the VPN server, which either grants the VPN client to log in or refuses a login request. The standard RADIUS solution is easy to employ (simply setup communication with the WOAS server on the application server) with no installation required for the WOAS agents. |
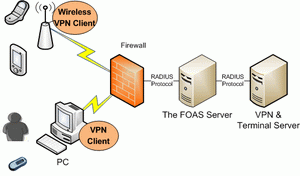 |
|
Outlook Web Access Protection
Applications such as the Outlook Web Access (OWA) Server can use the WOAS agent solution. Authentication requests are sent from the OWA Interface to the WOAS server through the WOAS OWA agent. When an end-user logs in, an OTP needs to be generated by the token and sent to the WOAS server through the WOAS OWA agent at the Web Interface. The authentication result will be returned to the OWA Server to decide whether to allow the end-user to log in. The WOAS OWA agent can be simply installed to seamlessly integrate with the OWA Interface so as to provide enhanced security. |
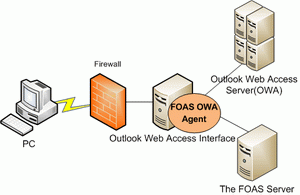 |
|
Domain Access Protection
Internally, a business may wish to integrate two-factor authentication, specifically OTPs into the domain access process, where the WOAS agent solution can be used. OTP Authentication requests and normal domain authentication requests are forwarded to the WOAS Server and the domain controllers to handle respectively. When an end-user logs in, an OTP needs to be generated by the token and input through the OTP interface provided by the WOAS domain agent. The authentication result of the WOAS server will be forwarded to the domain controller to decide whether the user is allowed to log in. The WOAS Domain agents will need to be installed at each domain PC that needs protection. |
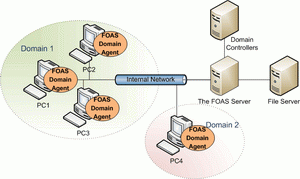 |
|
 |
|
 |
